Climate change and migrations: how climate is affecting borders
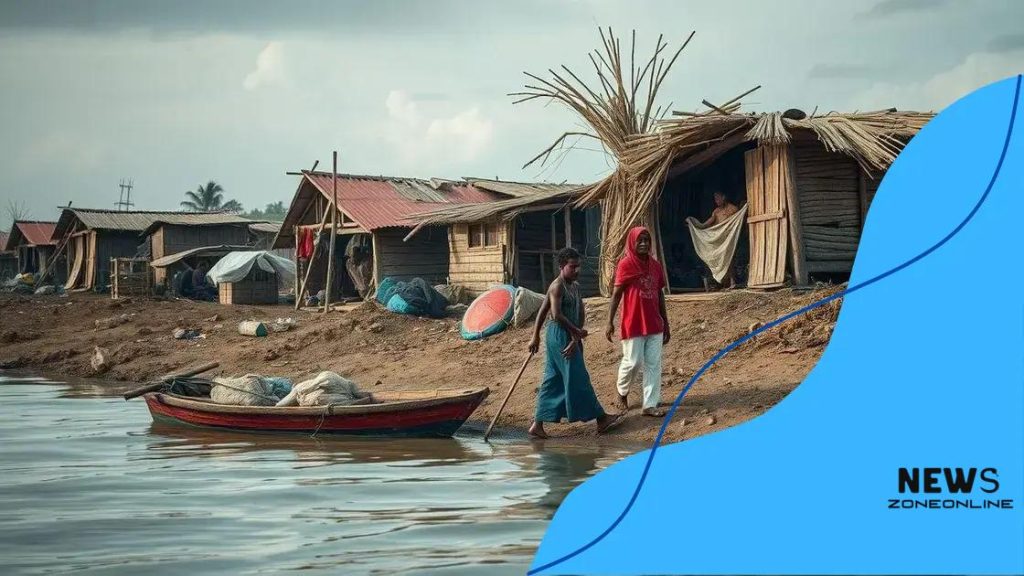

Climate change is significantly influencing migrations by displacing communities due to extreme weather events and rising sea levels, creating urgent challenges for both migrants and host nations.
Climate change and migrations are intricately linked and increasingly impacting lives worldwide. Have you ever considered how the shifting climate might redefine borders and force communities to adapt or abandon their homes? This conversation is more essential than ever.
The link between climate change and migration
As the world continues to grapple with climate change, its effects are increasingly evident in migration patterns. Weather events and environmental shifts are not just creating challenges at home; they are forcing people to seek new places to live. Understanding this connection is crucial for developing effective policies.
Impact of Extreme Weather Events
Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and floods, have devastated communities globally. These disasters leave people with no choice but to relocate. The loss of homes and livelihoods pushes families out of their regions, searching for safety and stability. This trend is becoming more common as climate change intensifies.
Rising Sea Levels
Another significant factor is rising sea levels. Coastal areas are particularly at risk, resulting in increased instances of population displacement. Communities near the shore may find their homes submerged, leading to mass migrations inland where they hope to find safety and opportunity.
- Vulnerable coastal regions are being lost.
- Increased flood risk disrupts daily life.
- Communities face long-term displacement.
While some regions are becoming uninhabitable, others are experiencing a surge in immigrants seeking refuge. This movement alters demographics and challenges national policies, leading to complex discussions about resource allocation and integration of newcomers.
In many cases, the communities that receive these migrants face their own challenges. Increased population can strain existing resources and infrastructure, creating tensions. Policymakers must address these issues while recognizing the root causes of migration linked to climate change.
To tackle this issue effectively, it’s essential to understand how climate change and migration interact. This insight can guide collaborative efforts between nations to manage the impacts of displacement and promote sustainable solutions.
Case studies of climate-induced migrations
Examining case studies of climate-induced migrations provides vital insights into how environmental changes lead to human displacement. Around the globe, different regions face unique challenges due to climate change, triggering movement and migration.
Hurricane Katrina
The devastation of New Orleans by Hurricane Katrina in 2005 is a crucial example. The storm caused floods and destruction, forcing thousands to leave their homes. Many of these individuals never returned, significantly altering the city’s demographics. They relocated to various states, impacting local economies and communities.
Bangladesh’s Rising Sea Levels
In Bangladesh, rising sea levels have displaced millions. Coastal communities are losing land due to erosion and flooding. Many families have migrated to urban areas in search of stability. Unfortunately, this rapid internal migration has led to challenges in cities such as Dhaka, including overcrowding and increased competition for jobs.
- Significant population loss in affected coastal regions.
- Pressure on urban infrastructure and services.
- Healthcare and education systems face increased demand.
Another notable example is the situation in the Sahel region of Africa. Droughts and desertification have made traditional farming difficult. Families are pushed to migrate to find more viable agricultural land or opportunities for work. This trend not only affects local economies but also contributes to social tensions between communities.
These case studies illustrate the far-reaching impacts of climate-induced migrations. Each situation reflects the struggle of individuals and communities adapting to changing environments. Understanding these patterns enables policymakers and organizations to create better strategies to support affected populations.
Impact on borders and national policies
The impact on borders and national policies due to climate-induced migrations is profound and complex. As more people are displaced by environmental factors, nations must adapt their policies to address these changing dynamics. The movement of individuals across borders poses both challenges and opportunities for governments worldwide.
Shifting Immigration Policies
Countries are reevaluating their immigration policies in light of increasing numbers of climate migrants. Some nations are beginning to recognize climate refugees and developing pathways for their legal status. This shift allows affected individuals to seek protection and support without facing legal barriers that traditionally apply to other migrants.
Border Security and Regulation
As the number of migrants grows, border security becomes a significant concern. Governments may choose to tighten regulations to manage the influx, impacting the freedom of movement. This situation can lead to humanitarian challenges, as more people become trapped at borders, seeking asylum but facing restrictions.
- Border regulations are becoming more stringent.
- Humanitarian aid often struggles to reach displaced populations.
- Access to resources is limited, increasing tensions.
Additionally, regional cooperation becomes essential as neighboring countries deal with shared issues related to climate migration. Collaborative policies can lead to more effective solutions and better resource management. For example, countries may work together on sustainable development initiatives that address the needs of both migrants and host communities.
The growing awareness of climate change’s impact encourages nations to take proactive measures. International agreements and frameworks are emerging to facilitate discussions about migration due to environmental causes. These conversations aim to create fair and humane responses for those affected by climate change.
Challenges faced by displaced communities
Displaced communities face numerous challenges that can significantly impact their lives. These challenges are often heightened by the circumstances surrounding their migration, especially due to climate change. As families and individuals seek safety and stability, they encounter various hurdles in their new environments.
Access to Basic Resources
One of the primary issues is the lack of access to basic resources. Displaced individuals may struggle to find adequate shelter, food, and clean water. In many cases, they arrive in areas where resources are already limited, leading to competition and increased tension with host communities.
Healthcare and Education
Healthcare services are often stretched thin in regions experiencing an influx of migrants. Many displaced people may not have access to necessary medical care, which can lead to worsened health conditions. Additionally, children in these communities face interruptions in their education. Schools can become overcrowded, making it difficult for all children to receive the education they need.
- Healthcare services are limited and overburdened.
- Educational opportunities are often disrupted.
- Host communities may lack resources to support newcomers.
Social integration can also be a significant challenge. Displaced communities may face discrimination or xenophobia in their new locations. This social isolation can affect their mental health and overall well-being, making it harder to rebuild their lives. Building relationships with local residents is crucial, yet it often requires overcoming significant barriers.
Furthermore, navigating legal systems presents complications for many migrants. They may struggle to understand their rights and face bureaucratic hurdles when applying for legal status or aid. This uncertainty can lead to anxiety and mistrust of the systems meant to assist them.
To effectively address these challenges, it is essential to foster cooperation between local governments, NGOs, and displaced communities. Collaborative efforts can provide the necessary support to help these groups thrive in their new environments.
The future of global migration trends
The future of global migration trends is influenced heavily by climate change, economic factors, and political situations. As the world continues to evolve, these elements shape how and where people migrate. Understanding these trends is essential for preparing societies for the changes ahead.
Climate Change and Migration Patterns
As climate change accelerates, we can expect to see an increase in the number of people displaced by environmental issues. Extreme weather events and rising sea levels may force entire communities to relocate. This migration will not only affect local areas but also lead to shifts in international migration routes.
Economic Opportunities
Economic factors will also play a significant role in determining future migration trends. Regions experiencing rapid economic growth may attract migrants seeking better job opportunities. As developed nations innovate and expand, they might see an influx of workers from countries with fewer prospects. This can create a dynamic where both sending and receiving countries must adapt to changing labor markets.
- Increased demand for skilled labor in growing economies.
- Impacts on wages and job availability in host countries.
- Potential brain drain in countries losing talent.
Political stability or instability can greatly influence migration as well. Areas with conflict or oppressive regimes may see high emigration rates, while peaceful nations may draw migrants seeking safety. International policies will need to adapt to this changing landscape, ensuring protection for vulnerable populations.
Furthermore, globalization has made it easier for people to move across borders. Technology allows for better connections and coordination among migrants. As communication improves, communities can maintain ties even when separated by vast distances. This connectivity may facilitate more coordinated responses to migration challenges.
In summary, the future of global migration trends will be shaped by an intricate web of factors, including climate change, economic opportunities, and political dynamics. Addressing these changes effectively will require international cooperation and flexible policy-making to support both migrants and host communities.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Climate Change and Migration
What role does climate change play in migration?
Climate change leads to extreme weather events and rising sea levels, displacing communities and forcing people to migrate to safer areas.
What challenges do displaced communities face?
Displaced communities often struggle with limited access to resources, healthcare, and education, as well as social integration issues.
How can countries adapt their policies to support migrants?
Countries can develop legal pathways for migrants, enhance humanitarian aid, and foster cooperation with local communities to support displaced individuals.
Why is global cooperation important in addressing migration?
Global cooperation is crucial to create effective solutions, share best practices, and ensure humane responses to the challenges posed by climate-induced migrations.





